Understanding the Vital Role of Edge Firewalls in Network Security
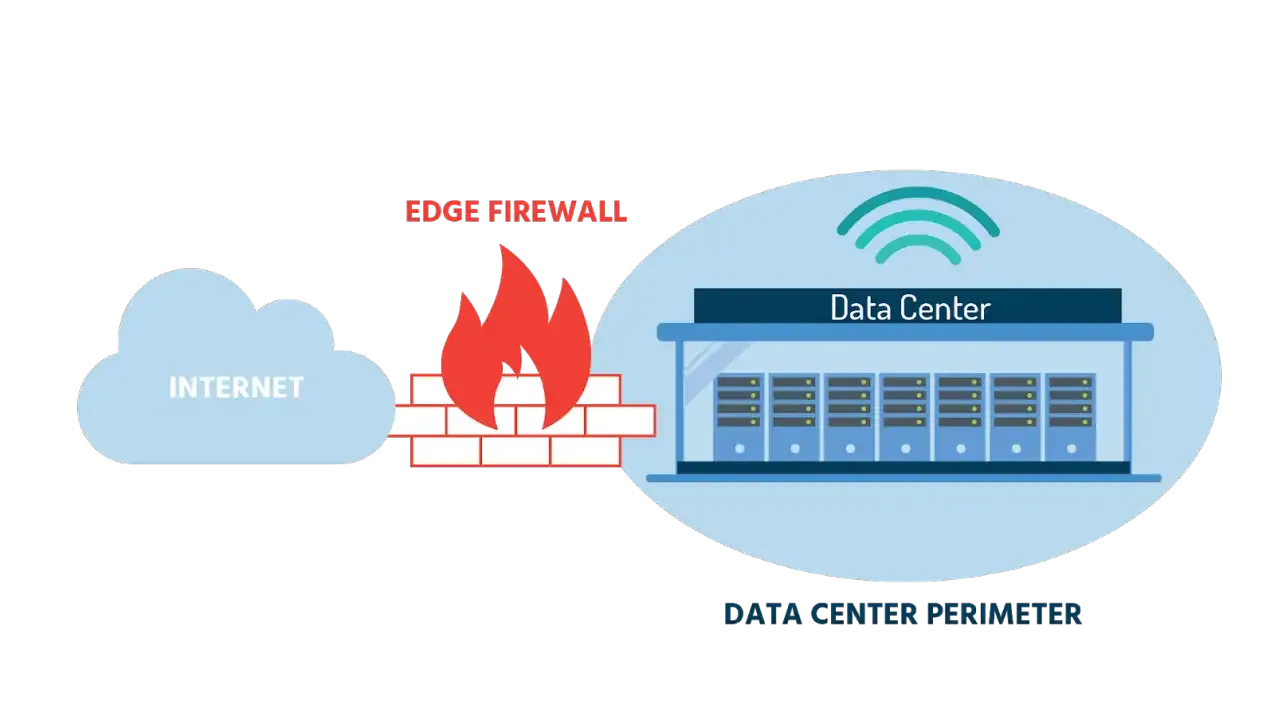
In the contemporary digital landscape, securing network boundaries is essential for businesses of all sizes. An edge firewall, also known as a perimeter firewall, plays a crucial role in this aspect. Positioned at the network's edge, it serves as a primary defense mechanism against external threats, managing and filtering traffic between a protected internal network and potentially harmful external networks.
What is an Edge Firewall?
An edge firewall is a security device that controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Located at the network's perimeter, it acts as a barrier that prevents unauthorized access, ensuring only legitimate traffic is allowed through.
Key Functions of an Edge Firewall
Packet Filtering
- Description: This technique inspects data packets based on criteria such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. Packets are either allowed or blocked based on these rules without examining the packet's content.
- Advantages: Packet filtering is efficient and fast, suitable for high-speed networks.
- Limitations: Limited to header information, making it less effective against sophisticated attacks using malicious payloads or spoofed addresses (Palo Alto Networks) (NordLayer).
Stateless vs. Stateful Filtering
- Stateless Filtering: Treats each packet independently, using header information for filtering decisions. While quick, it can miss threats that require context to detect (Lanner).
- Stateful Filtering: Monitors the state of active connections and uses context to make more informed decisions about incoming packets, enhancing security by understanding traffic flow and identifying anomalies (Lanner).
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Description: NAT firewalls hide internal IP addresses by allowing multiple devices on a local network to connect to the internet using a single public IP address, preventing direct attacks on internal devices from external threats (Illumio).
- Advantages: Enhances privacy and security by obscuring the internal network structure.
- Note: NAT works by translating private IP addresses of devices within a local network into a single public IP address when they access resources on the internet. This allows multiple devices within the local network to share the same public IP address, conserving public IP address space.
Proxy Firewalls
- Description: These firewalls act as intermediaries between internal users and the internet, inspecting and filtering traffic at the application layer. They are particularly effective for managing HTTP and FTP traffic by using deep packet inspection (Illumio).
- Advantages: Provide detailed inspection and filtering at the application level.
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs)
- Description: NGFWs combine traditional firewall capabilities with advanced features such as deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention systems, and application awareness. They offer a comprehensive security solution by integrating multiple security technologies (Illumio).
- Advantages: Enhanced threat detection and mitigation capabilities, making them ideal for modern network environments.